Angorithm4 Webinar #10
Co-host by Jiawei Wang 2021-12-24
1. 10th?
1. Intro to Performance Engineering
- 2021-10-15
- Hardware development (Complex)
- Matrix multiplication (Python
21041.67s-> Optimized C3.04s)
2. Intro to Computer Architecture
- 2021-10-22
- M1 Pro/Max Released
- RISC vs CISC
3. Comparision Sort I
- 2021-10-29
- Trade off in ISA (Semantic Gap)
- Merge Sort (Comparision Sort i)
4. Comparision Sort II
- 2021-11-05
- Dynamic Programming (Fds)
- Quick Sort (Comparision Sort ii)
5. Comparision Sort III
- 2021-11-19
- Virtual Machine
- Heap Sort (Comparision Sort iii)
- Lower Bounds of Comparision Sort (O(NlogN))
6. Microarchitecture
- 2021-11-26
- angorithm4.org
- Turing Machine (State)
- MIPS-Simulator and Eval (AST-Interpreter)
7. JavaScript. The Core
- 2021-12-03
- Prototype inherience
- Runtime
8. Intro to DataBase I
- 2021-12-10
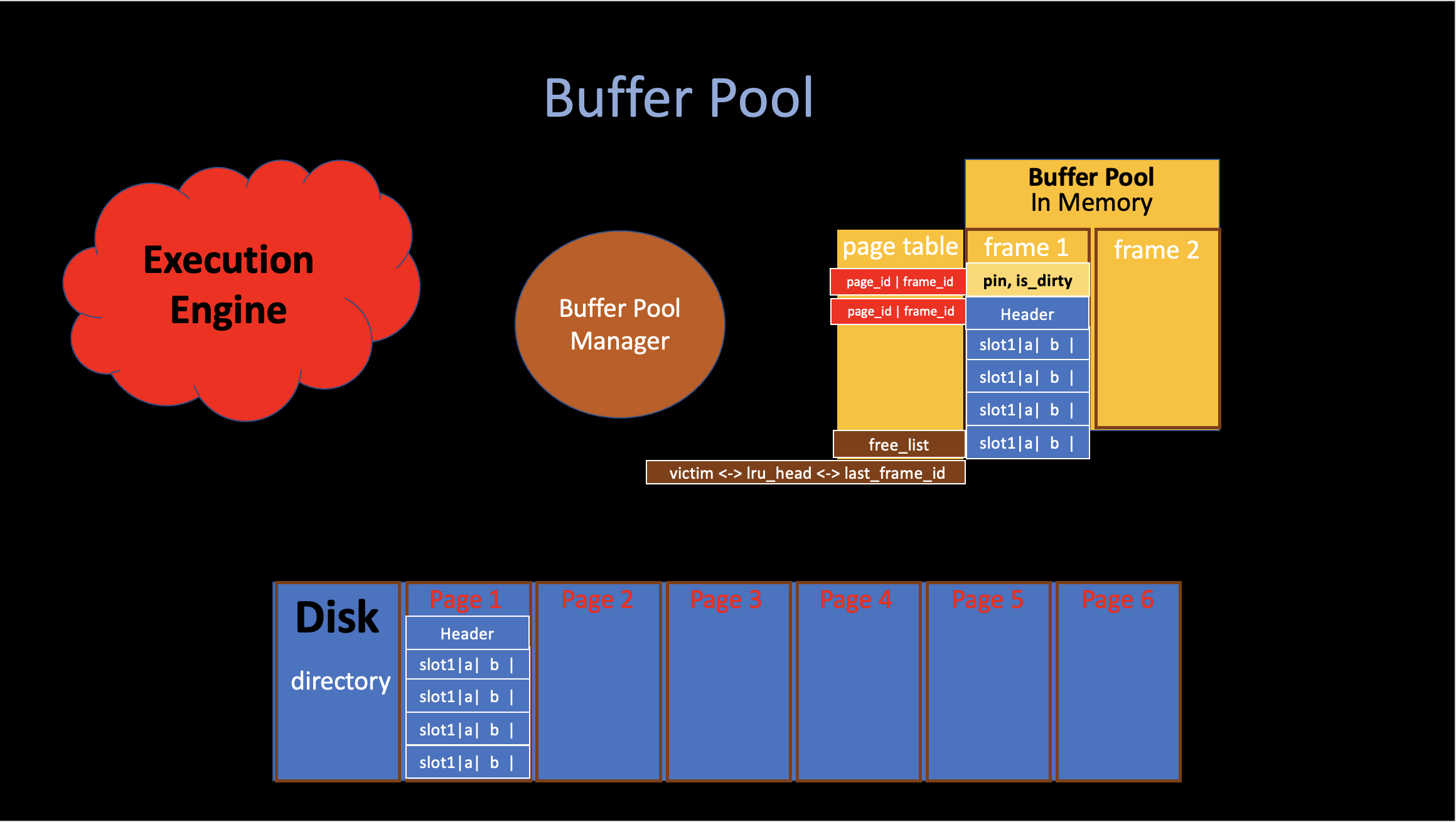
- Buffer Pool
- Hashing Part I (Static Hashing)
9. Intro to DataBase II and Digital Modulation
- 2021-12-17
- Digital Modulation
- Hashing Part II (Dynamic Hashing)
10. Intro to DataBase III
- 2021-12-24
- Below the DBMS VM
- B-Tree
2. B-Tree
Dynamic Hashing
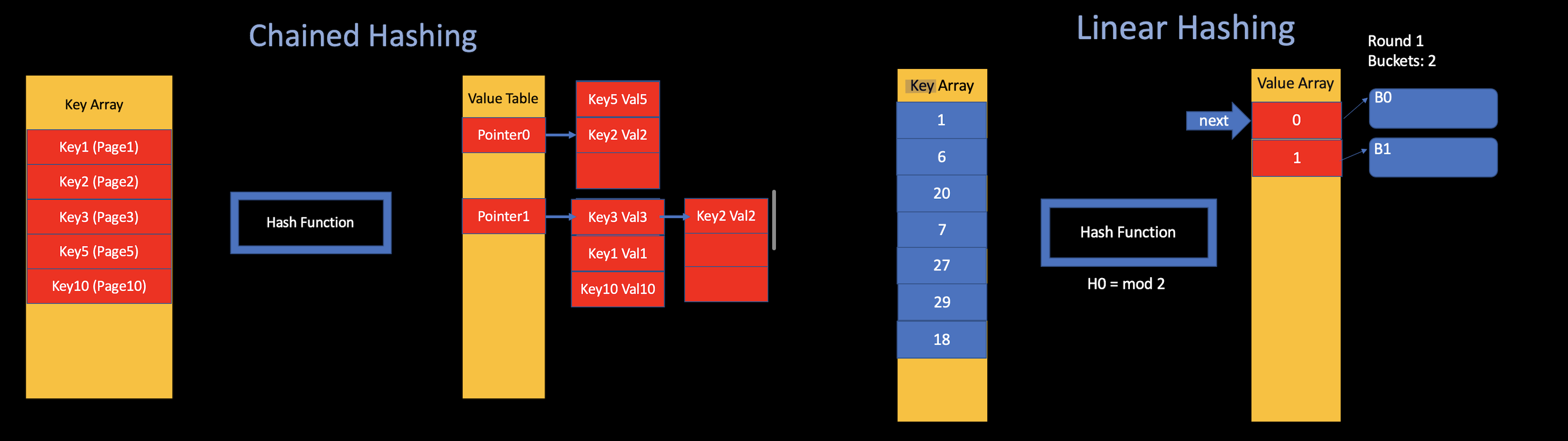
Trade off
Chained Hashing: Worst case O(N)
- Resolve collisions by placing all elements with the same hash key into the same bucket.
Extendible Hashing: Worst case O(1) + extra manage time
- “Only Split the chain when overflowed”
Linear Hashing: Same as Extendible Hashing, but take less time to manage it
- “Two Hash Functions”, Balance
What is a B-Tree?
- B Stands for Balance
- B- Tree (1971 Boeing)
- B+ Tree (1973 IBM)
- Blink Tree (1981 CMU)
A B-Tree is a self-balancing tree data structure that keeps data sorted and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in O(log n).
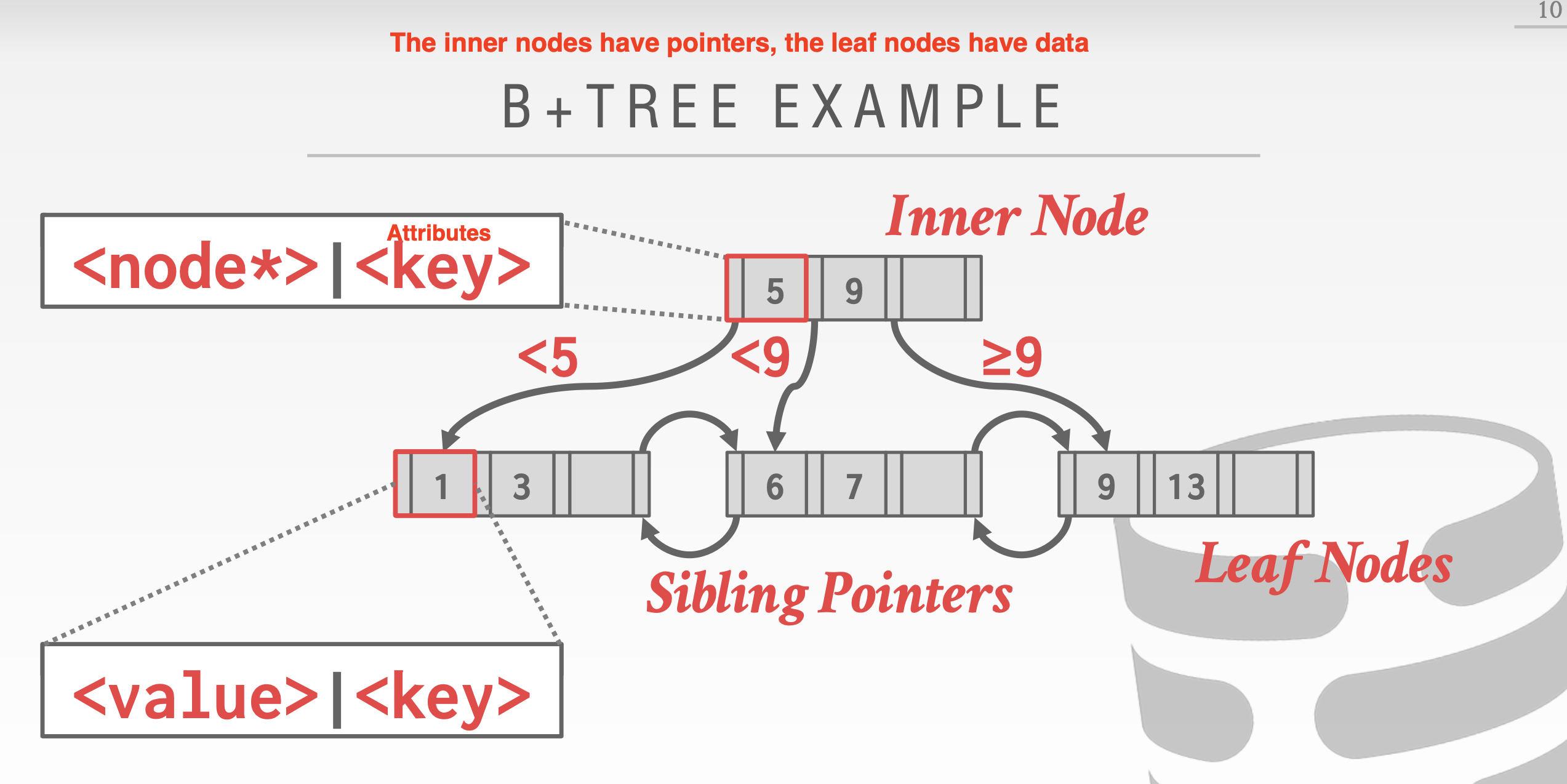
- The original B-Tree from 1971 stored keys + values in all nodes in the tree.
- A B+Tree only stores values in leaf nodes. Inner nodes only guide the search process.
- Like Binary Search Tree (Kind of)
Example: B+ Tree Visualization by David Gales
3. Below the DBMS VM
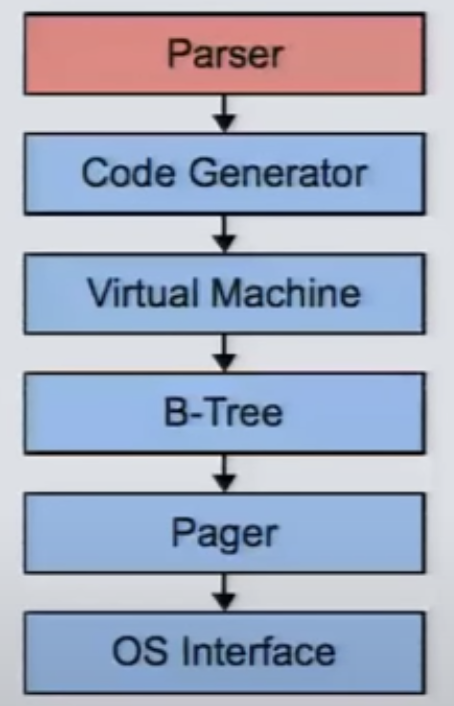
Video: D. Richard Hipp 2015 in CMU
What Happends Underneath?
emails_random.txt
ckenzie_Leigh5000@irrepsy.com
Chester_Zaoui4418@sheye.org
Gladys_Pratt1129@hourpy.biz
Vera_Driscoll43@cispeto.com
John_Smith9073@brety.org
Alexander_Brett1097@sheye.org
Phillip_May4129@hourpy.biz
Nina_Nicholls4940@kideod.biz
Johnathan_Needham5231@yahoo.com
Chad_Cox1524@twipet.com
Johnny_Eastwood9872@kideod.biz
Henry_Fleming7688@liret.org
David_Jenkin6789@twace.org
Angela_Foxley2732@fuliss.net
Jaylene_Rixon5612@qater.org
Lara_Snell8705@qater.org
Enoch_Clayton8217@zorer.org
Claire_Tindall9581@fuliss.net
Cristal_Tate2593@famism.biz
Erin_Eagle3884@eirey.tech
Caleb_Dubois1513@fuliss.net
Martin_Neal1410@nimogy.biz
Hazel_Dale9267@kideod.biz
Barry_Williams8002@hourpy.biz
Macy_Roth2551@eirey.tech
Irene_Kaur5056@twipet.com
Ethan_Newton6130@ovock.tech
Kieth_Warden8091@bretoux.com
Maria_Flynn2748@mafthy.com
Ronald_Palmer8118@kideod.biz
... 10000 lines1. Postgresql

$ sudo -u postgres psql postgres2. Create Table emails
CREATE TABLE emails (email VARCHAR(128));3. Import Data
COPY emails(email) FROM '/Users/Angold4/WorkSpace/Webinar/2021-12-24/src/emails_random.txt' DELIMITER ',' CSV;
4. Do some stuff:
Find all emails that begin with ‘A’
SELECT * FROM emails WHERE email LIKE 'A%';Count all emails that begin with ‘A’
SELECT count(*) FROM emails WHERE email LIKE 'A%';Find Min Email
SELECT min(email) FROM emails;SELECT * FROM emails WHERE email = 'Abbey_Chester9370@famism.biz';explain SELECT * FROM emails WHERE email = 'Abbey_Chester9370@famism.biz'; QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------
Seq Scan on emails (cost=0.00..199.00 rows=1 width=28)
Filter: ((email)::text = 'Abbey_Chester9370@famism.biz'::text)
Build a Hash Index
A table index is a replica of a subset of a table’s
attributes
that are organized and/or sorted for efficient
access using a subset of those attributes.
CREATE INDEX idx_emails_hash ON emails USING HASH(email); QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Scan using idx_emails_hash on emails (cost=0.00..8.02 rows=1 width=28)
Index Cond: ((email)::text = 'Abbey_Chester9370@famism.biz'::text)Build a B-Tree Index (Limitation of Hashing)
SELECT * FROM emails WHERE email like 'Abbey%';explain SELECT * FROM emails WHERE email like 'Abbey%'; QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------
Seq Scan on emails (cost=0.00..199.00 rows=1 width=28)
Filter: ((email)::text ~~ 'Abbey%'::text)CREATE INDEX idx_emails_tree ON emails USING BTREE(email);explain SELECT * FROM emails WHERE email like 'Abbey%'; QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Only Scan using idx_emails_tree on emails (cost=0.29..4.31 rows=1 width=28)
Index Cond: ((email >= 'Abbey'::text) AND (email < 'Abbez'::text))
Filter: ((email)::text ~~ 'Abbey%'::text)